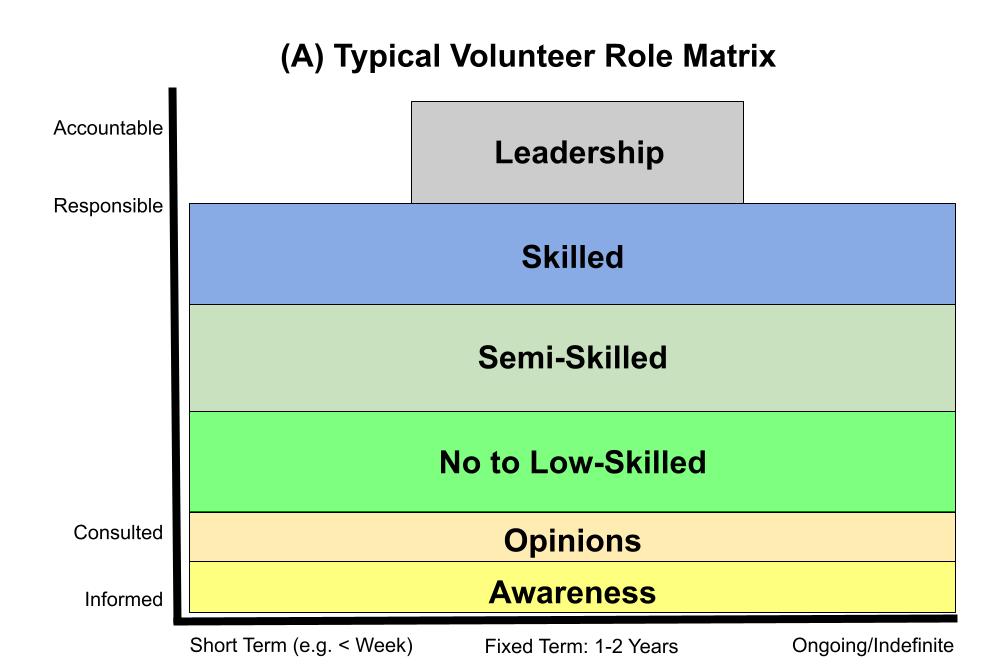
A Matrix that combines two dimensions to define volunteer roles. The dimensions are the length of time for the volunteer role and the classic ARCI responsibility matrix.

In an earlier post, Lucky 7’s in LAST VeGA, a volunteer lifecycle was introduced. An implicit assumption is that the organization knows what type of volunteer it is looking for. However, volunteers come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes; this model is a method to better define these differences.
Two Typical Dimensions to Categorize Volunteers
There are two different dimensions to categorize volunteers:
- Duration: What is the length of time a volunteer is expected to contribute to the organization?
- Event: Short duration, most often a day, a weekend, but a few weeks at the most.
- Fixed Term: A pre-defined term such as 1-2 years for a board member.
- Ongoing/Indefinite: No defined time period other than the health and enthusiasm of the volunteer and the continued existence of the organization.
- Episodic: A combination of the above but the volunteer is required on an ad hoc basis, for example, a Red Cross volunteer called out for emergencies.
- ARCI: sometimes known as RACI, what role the volunteer plays in the organization (italicized definitions from [1]).
- Accountable: Answerable for the correct and thorough completion of a task. These roles have legal, fiduciary, or moral obligations to the organization.
- Responsible: Those who do the work to complete the task. Within the above accountability, being obliged to deliver on something great or small. It might be as complex as feeding 2,000 hungry festival goers or as simple as ensuring cars are parked safely.
- Consulted: Opinions are sought via 2-way communications. Because of the person’s skills and experience, or because they are representative of a larger group of individuals.
- Informed: Kept up-to-date via 1-way communications. The person needs only be aware of organizational changes for which they will not provide an opinion (consulted) or have any influence over.
Categories Typically Overlap
There are nine types of volunteers. Although listed discreetly, they represent points along various continuums rather than mutually exclusive groupings. In addition, one person may fall into multiple groupings at the same time and during their tenure with the organization. The President of the non-profit may participate in a focus group and be the person carrying out the garbage at the end of an event.

| Category | Duration | ARCI |
| Board | Fixed Term (normally) | Accountable |
| Event Volunteer | Short Term, < 1 week | Responsible at varying skill levels |
| Project | Short to Medium Term, e.g. 1-6 months | Responsibility is exercised at varying skill levels. Some volunteers may be consulted or informed of the results |
| Ongoing Unpaid Volu-expert | Fixed Term or Ongoing | Skilled volunteer responsible for a critical aspect of the organization. Examples: bookkeeper, carpenter, legal, industry knowledge |
| Ongoing Unpaid Volu-ployee | Generally Ongoing | Low to semi-skilled volunteer responsible for an aspect of the organization. Their contribution can be learned and taken on more readily than the Expert. |
| Focus Group | Short Term, may be a standing group | Consulted on specific matters relevant to the organization. Skill or expertise varies. |
| Advisory Group | Fixed Term on Ongoing | Consulted on technical matters relevant to the organization. Typically highly skilled in their area of expertise or representative of a stakeholder group. |
| Information Sharing | Fixed Term on Ongoing | Informed of the activities of the organization. There is an expectation that the volunteer shares or acts on the information. |
| Honourific | Fixed Term on Ongoing | Ceremonial role in which they will be informed of organizational activities. The role has no responsibilities but may be consulted. |
Drawing the Dividing Line with Skill
The most contentious part of the model is the definition of the skill level. Remember, these are descriptions for a volunteer role, not of the volunteer taking on that role. A eminent ‘rocket surgeon’ may enjoy a low skill day at her daughter’s school.
Of course, we are not all ‘rocket surgeons’ or ‘brain scientists’ so the assumption is that the volunteer is average in the measures of intelligence, language (spoken, written) skills, social skills, and temperament. Allowances must be made for those who will take more time to catch on or may benefit from an accelerated orientation.
- No Skills
- No pre-existing knowledge is required, and training is provided.
- The role typically works under supervision of a more skilled volunteer to address any questions or circumstances not covered in the training.
- Briefing or training typically takes less than 2-hours to learn and practice the activities the volunteer is responsible for.
- Personal aptitudes are more important than training or experience (e.g. a friendly disposition is more important to the volunteer parking cars than ‘car parking theory’).
- Low Skills
- Some pre-existing knowledge or experience is helpful otherwise covered by an elongated training period.
- The role may supervise lower skilled volunteer roles but also works under the supervision of a leadership or more skilled role.
- Training requires 2-40 hours of cumulative time and is the combination of theory, practice, and experience in the role.
- Personal aptitudes play an equal and critical part in the success of the volunteer in this role.
- Semi-Skilled
- Pre-existing knowledge, certification, relevant education, or extensive experience is required for the role. This is combined with an extended apprenticeship with other Skilled and Semi-Skilled volunteers.
- This role supervises lower skilled volunteers and may also design the program of work.
- A combination of 40+ hours training, experience, apprenticeship, and/or certification is required to be fully qualified for this role. This is in addition to personal aptitudes.
- Skilled
- Extensive pre-existing knowledge, recognized certification, post-secondary education, and experience is required for these roles.
- These roles often require a professional (e.g. lawyer, accountant, medical) or vocational (e.g. electrical, personal-trainer) designation.
- This role might have supervisory functions and may only advise other roles on relevant legal, or technical matters.
- These roles typically require external certification although time spent with the non-profit may count towards experience hours required for students or professional development.
No to Low Skills, Small to Great Gifts
For most non-profits, most of your volunteer roles will fall into the Event or Ongoing time dimension and are ‘No to Low-Skilled’. For the non-profit, it is critical to remember that every hour donated to the simplest volunteer activity is a gift from an engaged person.
This model helps to categorize volunteers, it does not reduce the largesse shown or the need to treat the individuals involved with the utmost respect and admiration.
Typical Request for Comments
What are your thoughts, does the above cover the volunteers in your organization? Would you add, remove, or combine any? As always, leave me your thoughts.
References and Further Reading
- Responsibility assignment matrix, Wikipedia.

Pingback: A Spell (and Birch) Binding Use Case | Organizational Biology
Pingback: VMS, CPAs, and Volunteers – May 28, 2024 | Organizational Biology